(9.26 ~ 10. ? ) - 지금까지 리뷰 쓰는 것들 중에 가장 오래걸린다. 그만큼 사전지식같은게 좀 많이 필요한데
많은 부분을 서술하고싶어서 좀 오래걸리더라도 천천히 작성하겠다.
들어가기 앞서 먼저 본 논문을 읽기 전에 이전 논문과 다르게 더 많은 사전지식을 요구하는 느낌이 있어서 ( MViT 뿐만 아니라 다른 용어 등등.. )
내가 찾아 보았던 블로그에서 도움을 받으면 좋을 것 같아서 적어둔다.
이 논문을 읽으면서 swin Transformer 논문을 같이 읽고 있었는데 , 특히 자주 나오는 용어들이나 개념들이 있는 것 같아서 서 ( 아마도 다들 알고있다고 가정하고 쓰는 용어 같은데.. 나는 읽기 전까지는 몰랐기 때문에.. ) 노션에 말고 여기다가 정리해서
https://darkpgmr.tistory.com/137 : scale 과 img pyramid 에 대해서 설명해주는 글이다. 이분 블로그는 특히나 NeRF 를 공부하기 위해서 기본적인 Geometry 공부하기 위해서 자주 참고하는데 글 퀄리티가 정말 좋다.
+ https://devbasket.tistory.com/21 : scale 과 resolution 의 관계가 궁금해서 찾아보았다.
scale 에 대한 이해 => 여기서 resolution 과 관계가 있구나
스케일이 커지면 -> (대체로) 이미지 size 가 작아짐
그럼 scale 과 resolution 의 관계는 ? -->
resolution & channel size <-> computing 과 어떤 관계가 있는지 헷갈렸었는데.. -->
-----
사전지식이 좀 많이 필요하다
FPN , SWIN , MVIT 이거 한번씩 더 읽어봐야 할 것같다.
Abstract
본 논문에서는 image and video classifciation & object detection 을 위한 Multisalce Vision Transform (MViTv2) 를 제안합니다. 기존 MViT 에서 decomposed relative positional embedding 과 residual pooling connection 을 도입한 모델인 MViTv2는 accuracy & compute 에서 더 좋은 성능을 보여주었습니다. 또한 모델은 3가지 domain 에서 SOTA 성능을 보여주었습니다. ( ImageNet classification (88.8%) , 58.7 AP on COCO dataset , 86.1% on kinetics-400 video classification )
1. Introduction
다양한 visual recognition task 를 위한 architectures 를 설계하는 것은 역사적으로 매운 어려운 일인데, 가장 널리 쓰인 모델은 간단하면서도 효율적인 모델을 combine 시킨 모델들 이였습니다 ( VGGNet and ResNet ) . 최근 Vision Transformers(ViT) 는 CNN 과 경쟁적으로 사용될 정도로 괜찮은 성능을 보여주고 있을 뿐 아니라 다른 vision tasks 에서 사용될 수 있도록 모델들이 발전되고 있습니다.
ViT 는 image classification 에서 쓰이고 있지만, high-resolution object detection & space-time video understanding tasks 에서는 여전히 사용하기 어렵습니다. Transformer based 모델들은 self-attention blocks 으로 인해서 scale에 따라서 연산량과 메모리가 quadratical complextiy 하게 증가 하게 됩니다. (ViViT 에서도 이 문제를 해결해보기 위해서 다양한 방법들을 시도했었습니다. ) 이를 해결하기 위해서 최근 두가지 다른 방법을 사용했는데 (1) local attention 을 사용한 swin Transformer ( 인용수가 10000회를 넘어가네요 ) , (2) pooling attention 을 사용한 MViT 두가지 방법이 있습니다.
MViT 는 ViT 를 확장하는 방식으로 아키텍쳐를 구성합니다. 처음부터 high-resoltuion 를 가지는게 아니라 low-resolution to high-resolution 으로 가는 여러 단계를 거쳐 모델을 구성하게 됩니다. MVIT는 video tasks 에서 SOTA 급 성능을 내고 있습니다.
본 논문에서 저자는 두가지 간단한 techincal improvement 를 통해 성능을 향상시키고 , MViT 가 spatial 뿐만 아니라 spatiotemporal recogintion ( 간단하게 말하면 video & img 에서 잘 작동하는지 확인하기위해 )을 위한 back bone 역할을 수행 할 수 있는지 확인하기 위해서 3 tasks ( image classification , object detection , video classification ) 를 수행합니다.
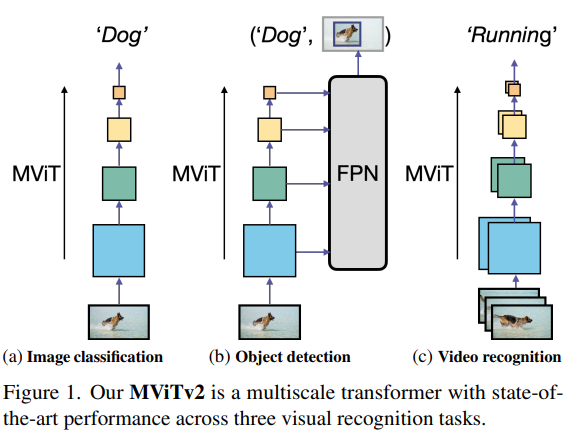
(i) We create strong baselines that improve pooling attention along two axes
(a) shift-invariant positional embeddings using decomposed location distances to inject position information in Transformer blocks
(b) a residual pooling connection to compensate the effect of pooling strides in attention computation.
두가지 간단한 방법을 통해서 성능을 향상시켰습니다.
(ii) Using the improved structure of MViT, we employ a standard dense prediction framework: Mask R-CNN [36] with Feature Pyramid Networks (FPN) [53] and apply it to object detection and instance segmentation.
FPN 을 도입해 기존 MViT를 향상시킨 구조를 object detection & segmentation 에서 사용한다고 합니다.
+ MViT 에서는 FPN 이나 SSD 처럼 피라미드 구조를 사용하지 않는 것으로 아는데 MViTv2 에서는 이런 피라미드 구조를 사용하나 봅니다.
(FPN 에 대한 더 자세한 설명은 https://herbwood.tistory.com/18 에서 참조 )
MViT 가 계산&메모리 비용을 극복하기 위해서 pooling attention을 사용하여 high resolution 을 처리하는지 연구합니다.
여기서 멈추는게 아니라 본 논문에서는 Hybrid window attenti on을 사용하여서 더 좋은 정확도와 compute 를 사용 할 수 있다고 합니다.
(iii) We instantiate our architecture in five sizes of increasing complexity (width, depth, resolution) and report a practical training recipe for large multiscale transformers. The MViT variants are applied to image classification, object detection and video classification, with minimal modification, to study its purpose as a generic vision architecture.
2. Related Work
3. Revisting Multiscale Vision Transformers

MViT v1 은 low - & high- level visual modeling block( Vit 로 구성된 ) 들로 구성되어 있습니다. MViT는 input 단계에서 output 단계까지 해상도(sequence length) L를 줄이는 동시에 channel width D 를 천천히 확장합니다.
( 정확히 어떤말인지 아직 파악이 안되어있는데 아마도 : MViT 에서 각기 다른 view 를 병렬적으로 처리하는 느낌인데(피라미드 구조와 다르게) 이렇게 처리하면서 channel width 는 늘리면서 , view 를 순차적으로 fusion 하면서 그냥 concat 할때보다 sequence 를 줄인다는 의미이거나 아니면 global encoder 에서 각 view 별로 cls token 을 추출하니까 이때 sequence 가 줄어든다는 의미 일수도 있을것 같습니다. )
(+ 수정 : MViT 논문에 그대로 있는 말이였네요.
)
transformer block 을 down sampling 하기 위해서, MViT 는 pooling attention 을 도입했습니다.
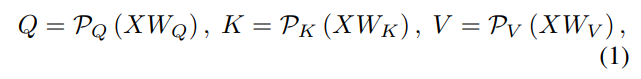

구체적으로, input X 에 Linear projections 을 하는건 기존 Transformer 와 방법이 동일하지만
MHPA(multi-head pooling attention) 에서는 query,key,value 를 pooling operator(P) 를 거칩니다.
이렇게 되면 length L 은 pooling operator 로 인해서 감소된 legnth 를 가지게 됩니다.
Z 는 flexbile length L ( 길이가 길다면 pooling 으로 줄여줄 수 있기 때문: video 에서 유용 ) 를 가지는 output 을 만들게 됩니다.
Pooling attention 을 사용하면 query tensor Q를 pooling하여 MViT의 resolution 을 줄일 수 있으며, K (key)와 V(value) tensor를 pooling하여 computing 및 memory complexity을 크게 줄일 수 있습니다.
+ ( 그렇다면 왜 resolution 이 줄어들까? )
4. Improved Multiscale Vision Transformers
4.1. Improved Pooling Attention
MViTv2의 두 가지 중요한 의미(abstract 에서 다루었던) 를 소개하면서 진행합니다.
Decomposed relative position embedding.
mvit 는 token 간 interaction 을 모델링 하는 능력을 보여주었지만 sturcture 보다는 content 에 중점을 둡니다. space-time sructure 모델링은 위치 정보를 제공하기 위해서 "absolute" positional embedding 을 사용합니다. 이 임베딩은 vision 의 shift-invariance 의 기본원리를 무시합니다. 즉,MViT 가 두개의 patch 간의 상호작용을 modeling 하는 방식은 relative position 이 달라지지 않더라도 absolut position 에 따라서 변경됩니다. 이 문제를 해결하기 위해서 본 논문에서는 pooled self-attention computation 에만 depend 하는 relative positional embedding 를 사용합니다.
(shif-invariance 의 기본원리란?)
두개의 Input i & j 사이의 relative position 를 위치 임베딩 R_p(i),p(j) ∈ R 로 encode 합니다. 여기서 p(i) p(j) 는 i 와 j 의 spatio(or spatiotemporal ) position 을 나타냅니다.
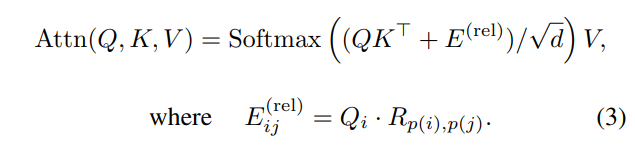
하지만 가능한 임베딩수 R_p(i),p(j) 는 O(THW) 로 확장되기 때문에 컴퓨팅이 많이 필요하게 됩니다. 이런 complexity 를 줄이고자 , 본 논문에서는 spatioemporal 축을 따라 i 와 j 사이의 거리를 decompose ( 분해 ) 합니다.
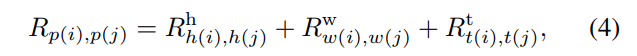
R_h,w,t : positional embedding height , width , temporal axes
h(i) , w(i) , t(i) : token of verical , horizon , temporal
R_t 는 video case 에서만 사용되는 temporal dimension 을 support 하는데만 사용됩니다.
이렇게 decompose 함으로써 기존 O(TWH) 에서

위와 같이 임베딩 수를 줄여서 초기 단계에 High-resolution feature map 에 큰 영향을 미칠수 있습니다 (--> 근데 왜..?)
Residual pooling connection
MViT(v1)에서 확인했듯이, pooling attention은 메모리 요구량과 computation complexity 를 줄이는데 매우 효과적입니다.
MViTv1 에서는 Q tensor 의 stride 보다 k & v tensor 에서 더 큰 stride 를 가지며 output sequence resolution이 단계를 걸쳐 변경되는 경우에만 downsampling됩니다.
This motivates us to add the residual pooling connection with the (pooled) Q tensor to increase information flow and facilitate the training of pooling attention blocks in MViT. --> MViT 다시한번 확인해봐야될듯 먼소린지 모르겠네

본 논문에서는 새로운 residual pooling connection inside attention block (Fig 2) 을 제시합니다.
오른쪽 그림 보시면 Query tensor 를 output sequence Z 에 더해주는 모습을 볼 수 있고 아래 수식과 같이 나오게 됩니다.
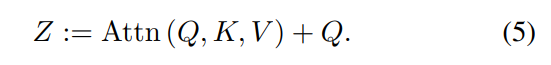
ablation study 실험 결과에서 확인할 수 있는데 pooling operator(P_Q) and reisdual path 는 제안한 residual pooling connection 에서 꼭 필요하다고 합니다. 이 변경은 Eq (5)에 풀링된 쿼리 시퀀스를 추가하는 데 비용이 적게 들기 때문에 키 및 값 풀링의 큰 발전으로 복잡성이 낮은 어텐션 계산을 여전히 누리고 있습니다 <-- 이문장 수정필요..
4.2. MViT for Object Detection
이번 섹션에서는 어떻게 object detection adn instance segementation task 에서 MViT backbone 을 적용하는 방법에 대해서 소개하고자 합니다.
FPN integration

( FPN 에 대한 더 자세한 정보는 : https://herbwood.tistory.com/18 참고 )
hierarchical 구조의 MViT 는 4개의 stage 로 multiscale feature map 을 생성하는데 , 이는 자연스럽게 object detection 에서 사용하는 Featrue Pyramid Network (FPN) 을 사용하게 됩니다. ( 근데 FPN 을 쓸려고 feature map 을 4단계로 나눈거아니야?... 내가 번역 뉘양스를 잘못 파악한걸지도.. ) Top-down payramid with lateral connection in FPN 는 모든 스케일에서semantically strong (의미론적으로 강한..? ) 한 feature map 을 가진다 ( https://blog.naver.com/PostView.nhn?blogId=tomatian&logNo=221865008339 참고) . MViT 백본과 함께 FPN을 사용하여 이를 다양한 감지 아키텍처(ex: Mask R-CNN )에 적용합니다.
--> FPN 에 대해서 좀 더 자세히 읽어보고 다시정리.
Hybrid window attention.
Transformer 는 quadratic complexity 를 가지고 있습니다 ( o(n^2 * d )-token 수에 따라 증가) . 이러한 문제점은 object detecion의 경우 더 악화되는데, object detection 에 경우 high resolution input & feature map 을 필요로 하기 때문입니다.
본 논문에서 두가지 방법을 사용해 compute & emory complexity 를 감소시킵니다.
1. the pooling attention designed in attention blocks of MViT.
2. window attention used as a technique to reduce computation for object detection in Swin
이 두가지 방법(pooling attention & window attention) 은 모두 self-attention 을 계산할때 query,key,value 및 tensor size 를 줄여 self-attention 의 complexity 를 control 합니다. 하지만 둘의 본질적인 특성은 다릅니다.
Pooling attention 은 local aggregation 을 통해 downsampling 하지만 global self-attention computation 은 유지합니다.
반면, window attention 은 tensor 의 resolution 을 유지하지만 input 을 non-overlapping winodw 로 나누어 local 로 self-attention 을 수행한 다음 각 window 내에서 local self-attention 만 계산합니다 (swim transformer 참고).
두 방식의 차이점은 object detection task 에서 보완적인 작업을 수행 할 수 있는지 연구하도록 motivation 합니다.
( 두 방식의 발전된 형태를 제시 할꺼라는 뜻 )
--> 애초에 high resolution 이 되면 self-attention 이 하기 힘들다는 것을 논의의 시작으로 swim transformer 가 개발됨
swim transformer 도 더 읽어봐야 정확한 문제점을 알 수 있을듯 ?
window attention 은 windows 내에서 local self-attention 을 수행하기 때문에 다른 window 간의 connection 이 부족합니다.
이런 문제를 해결하기 위해 Swin 에서는 shifted windows 를 사용하지만 ,본 논문에서는 Hybrid windows attention(Hwin)에서는 Cross-window connection 을 제시합니다.
Hwin 은 window 내에서 local attention 을 모두 계산하지만 , 마지막 block에 마지막 3 stage 에서는 FPN 에 feed 해줍니다. 이런 방식으로 , input feature 들은 FPN의 global information 을 포함하게 됩니다. ( local & global 모두 가질 수 있게 됩니다)
positional embeddings in detection
고정되어 있는 Resolution(224x224) 을 Input 으로 사용하는 ImagNet classification 과 다르게, object detection 은 다양한 크기의 input size 를 가지게 됩니다.
MViT 의 positional embedding 의 경우, 먼저 input size 가 224x224인 positional embedding 에 해당하는 imageNet pre-train weight 에서 parameter 를 초기화 한다음 object detection trainig 을 위한 해당 크기로 interpolate (보간 - 문맥으로 보면 아마 새로운 사이즈로 다시 학습해서 parameter 를 학습시켜준다.. 정도로 이해하면 될 것 같습니다 ) 합니다.
'Paper' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [paper review] BLIP: Bootstrapping Language-Image Pre-training for Unified Vision-Language Understanding and Generation (3) | 2025.01.13 |
|---|---|
| [paper review] Meshed-Memory Transformer (3) | 2024.12.24 |
| ViViT: A Video Vision Transformer 리뷰 (0) | 2023.09.08 |
| Non-local Neural Networks 리뷰 (+ code review ) (3) | 2023.08.20 |
| Quo Vaids, Action Recognition? A New Model and the Kinetics Dataset (2018) (1) | 2023.08.11 |
